Data Integrity in Pharmaceutical Industry refers to the accuracy, consistency, and dependability of data in a database or any other information storage system.
The
integrity of information is crucial in pharmaceutical manufacturing sector for
a variety of reasons, including safety of patients, legal compliance with the
regulations, and business profitability.
Principle
of Data integrity:
ALCOA (Attributable Legible Contemporaneous Original Accurate) is a framework that is required for the implementation of Good Documentation Practices (GDPs) and is utilized by regulated enterprises to ensure data integrity. Electronic and paper data are both addressed by ALCOA. The ALCOA principles are essential for promoting data integrity initiatives, upholding GDPs, adhering to GMPs, and keeping an electronic and paper data handling throughout the lifespan that meets the requirements. The acronym ALCOA, was first used in the 1990s by Stan W. Woollen of the FDA's Office of Enforcement.
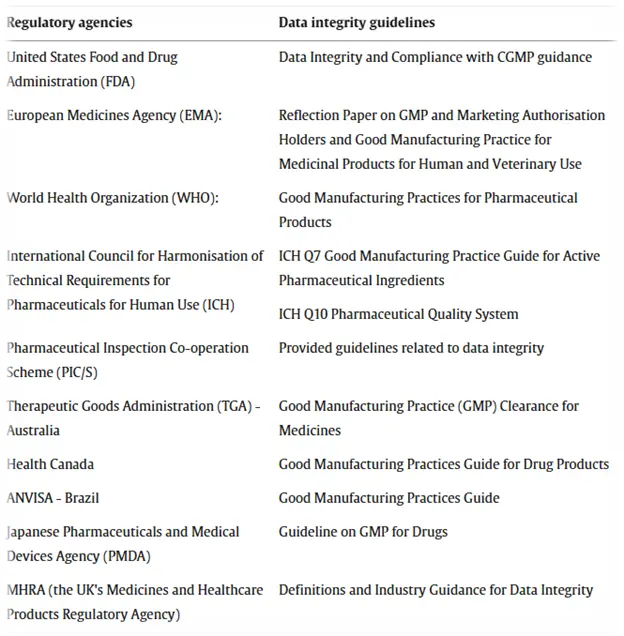
International
regulatory guidelines
Regulatory
agencies worldwide have established guidelines and recommendations for assuring
the reliability of data in the health care sector. These guidelines insist on
how crucial it is to keep precise, complete, and trustworthy data throughout
the entire span of a pharmaceutical product's lifecycle.
Data
Integrity errors:
Data
integrity errors can be categorized into two main types based on whether they
are intentional or unintentional
Preventing
and Addressing Errors:
ü Implementing
robust data validation and verification processes.
ü Regularly backing up data
to mitigate the impact of potential errors.
ü Training users to follow proper data
handling practices.
ü Authorization systems and entry restrictions
in a place to prevent unwanted access must be established.
ü The
Data should be encoded to avoid manipulation while it is being
transmitted or stored.
ü The
users should be educated about security best practices and the risks
associated with intentional data manipulation.
Standard operating procedure for data integrity and error free documentation with their tractability to the original data generated by the computer systems.
1. OBJECTIVE
To lay down a procedure for data integrity for documentation.
2. SCOPE
This procedure is applicable to all departments of the manufacturing facility.
3. RESPONSIBILITY
Chemist/ Ofcer/ Executive
4. ACCOUNTABILITY
All Department Heads/ QA Head
5. PROCEDURE
5.1 Data Integrity shall be maintained in all manual or system generated electronic data.
5.2 Data should be complete and accurate without any alteration.
5.3 Any identied data integrity issue shall be handled as per the quality management system and proper
5.4 Action shall be taken on the generation of false data or modication of data.
5.5 Data generation and processing should follow the time sequence.
5.6 Data shall follow the rules of ALCOA i.e. attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original and accurate.
5.7 Data should readable and complete.
5.8 Data shall be veried and approved by a competent technical person.
5.9 Instruments having audit trial shall be reviewed daily before approval of data and shall be checked for any abnormalities.
5.10 Data generation and recording or processing on behalf of another person shall be avoided.
5.11 All clocks used to record time data should be synchronized and controlled (time and date should not be changed).
5.12 Softwares and computer systems used in data recording and processing should be validated.
5.13 Processed and computer-generated data must have the electronic signature of the user, reviewer and approver and signature must be secured.
5.14 All data should be traceable to its processing and modication. All original raw data shall be stored. 5.15 For instruments those have only printed data output, print out shall be considered as raw data and for the instruments store electronic data, the stored data les shall be considered as raw data.
5.16 Data error found during the review shall be corrected with proper justication.
5.17 Any paper or electronic data modication shall be attributable.
5.18 Data can be excluded only after proper scientic justication and original data shall be stored for traceability.
5.19 Reconciliation of issued documents like logbooks, protocols, batch manufacturing records, change control and deviation forms shall be done wherever it is applicable.
5.20 System suitability data from instruments like HPLC and GC shall be stored and documented.
5.21 Original data shall be stored as per the company policies and shall be destroyed with the reported data.
5.22 Unauthorized assess to the computer systems shall be prevented by giving the assess rights as per the responsibility and role of the user.
5.23 User department shall not have rights to alter the data les only IT person shall have rights to alter and delete the data les.
5.24 Computer system users shall not share their logins and shall not access computer systems on behalf of others.
5.25 Backup of data shall be taken periodically and the backup and recovery process shall be validated.





.webp)



%20Web%20of%20pharma%20.webp)

%20webofpharma.JPG)


